Could You Design Quora's Database? A Journey Through Scaling Challenges
Unlock the secrets of database scaling and optimization used by tech giants like Quora. Discover techniques to manage your own growing data sets.
Imagine this: Quora handles a staggering 400 million users and over 100,000 requests every single second! How does a website where questions, answers, and ideas flow endlessly manage such a massive amount of data?
If you've ever wondered about the technology behind Quora (especially that 13 Terabyte database! in 2023), then let’s see in this article.
We'll explore how Quora might have tackled the challenges of scaling its database from its early days to the powerhouse it is today.
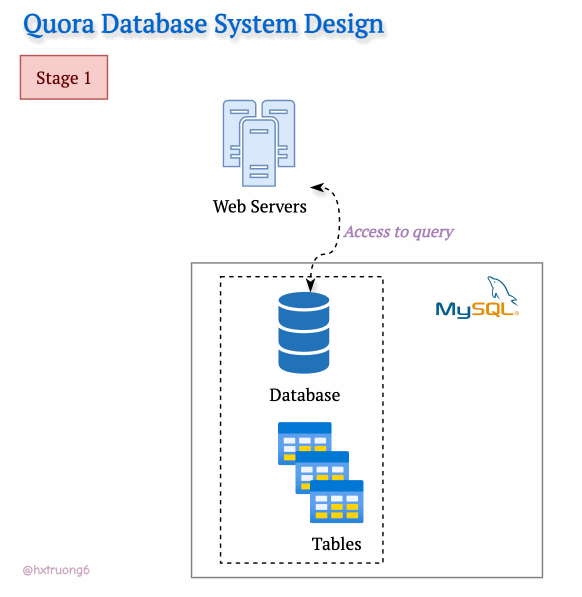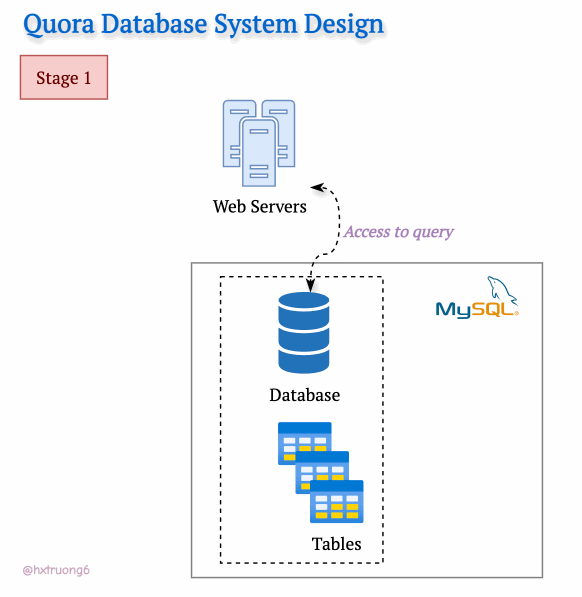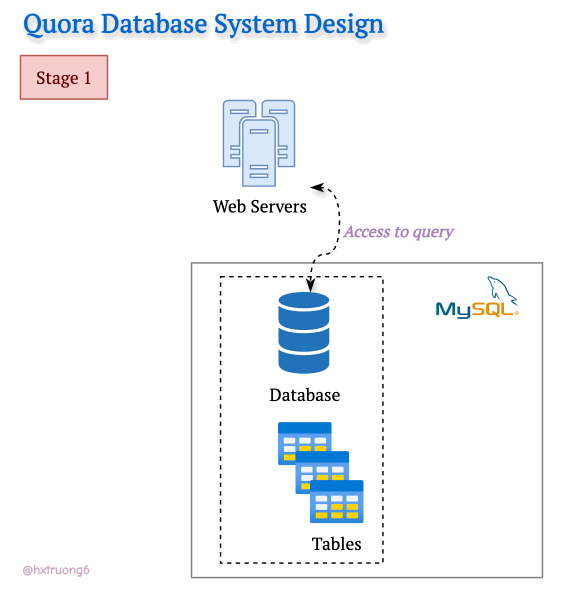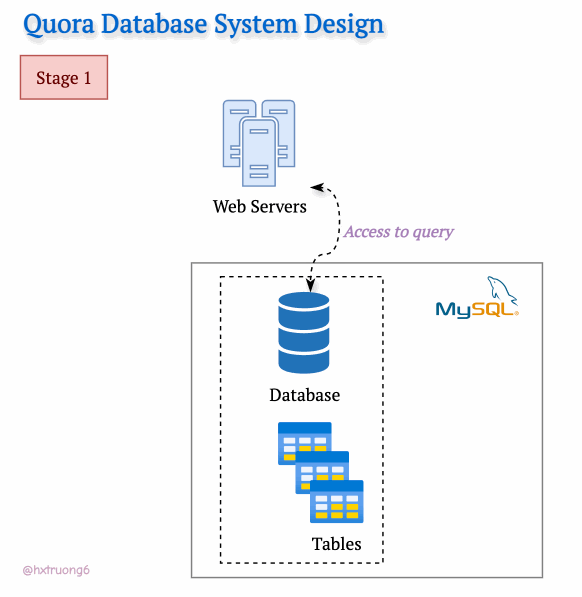
In the Early Stage
With a smaller user base in its early days, Quora's technical needs were likely simpler. A single web server and a trusty MySQL database could likely be handled the initial traffic.
Curious Section: How the database structure could be designed at this level? We don't have Quora's original blueprints, but let's brainstorm what a basic schema might have looked like...
Hint: Think about the core elements: questions, answers, users, upvotes...
Later On...
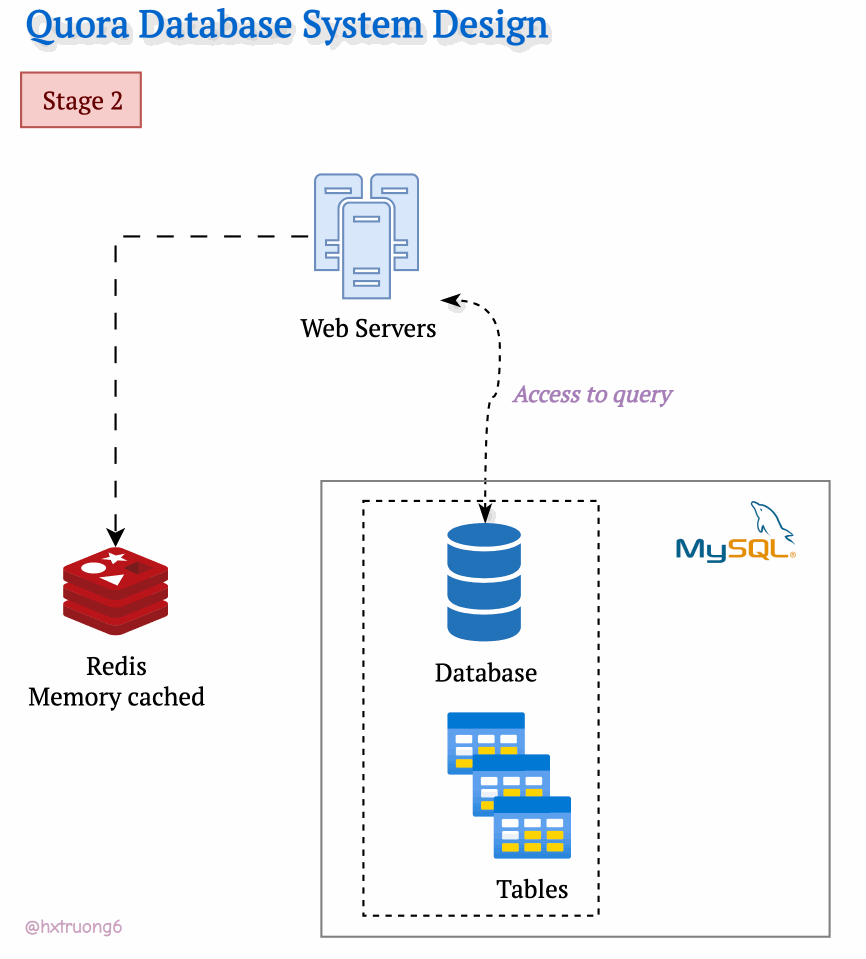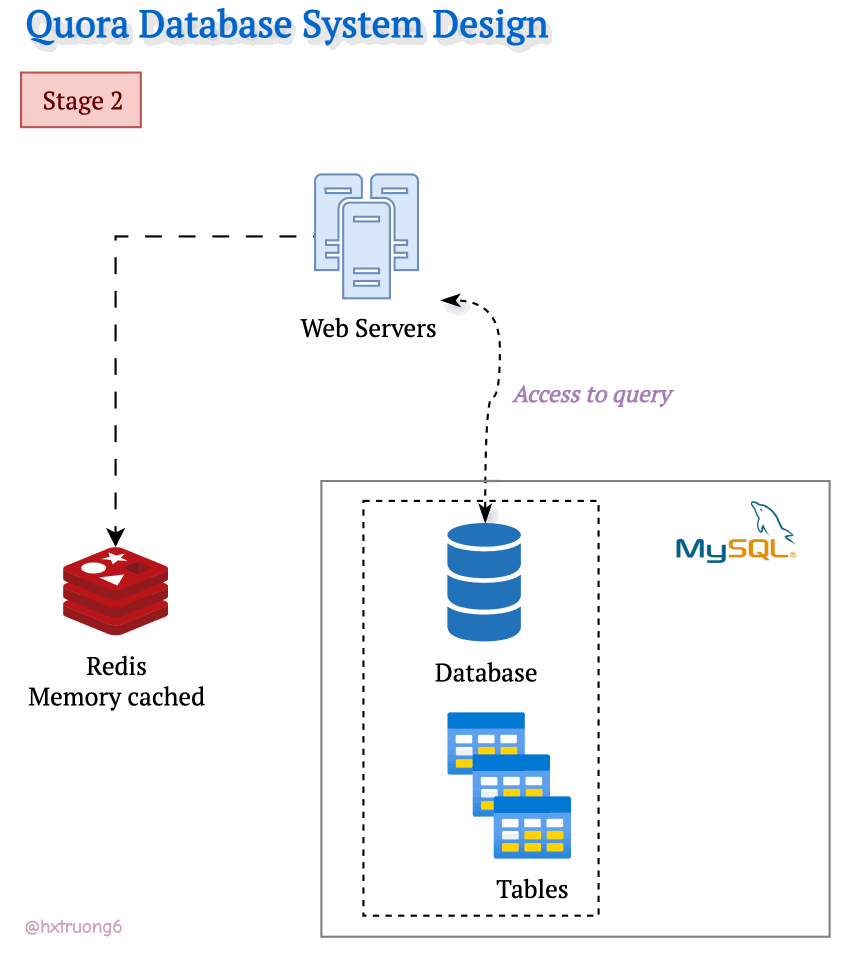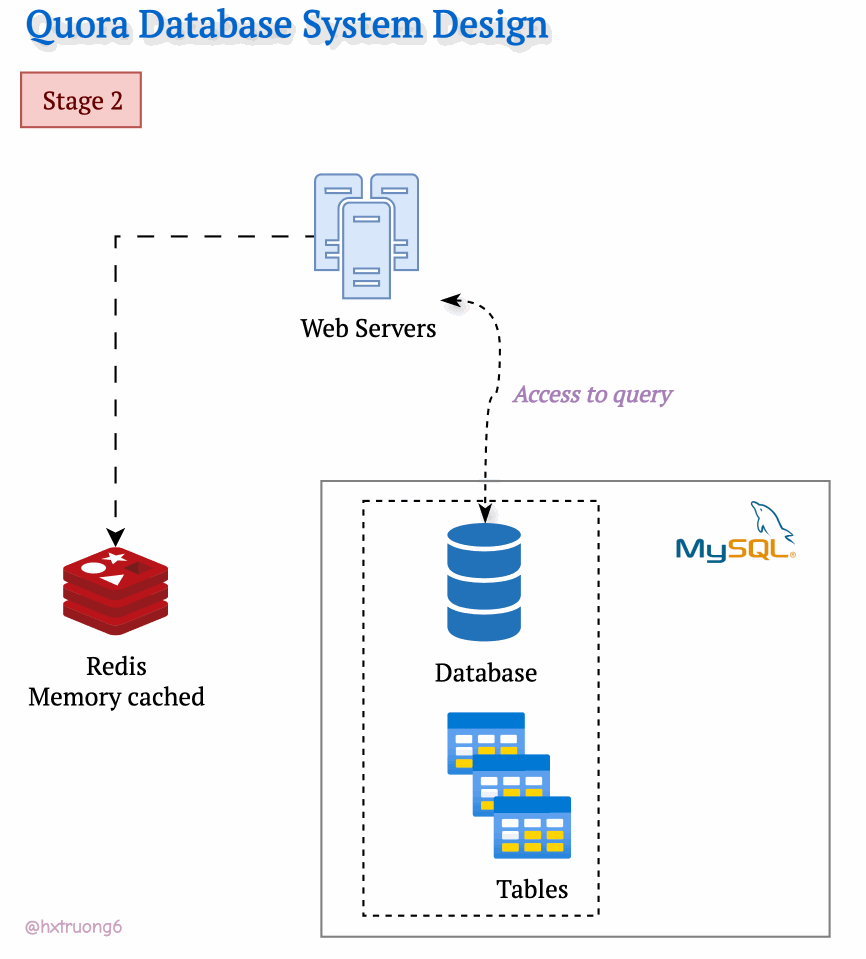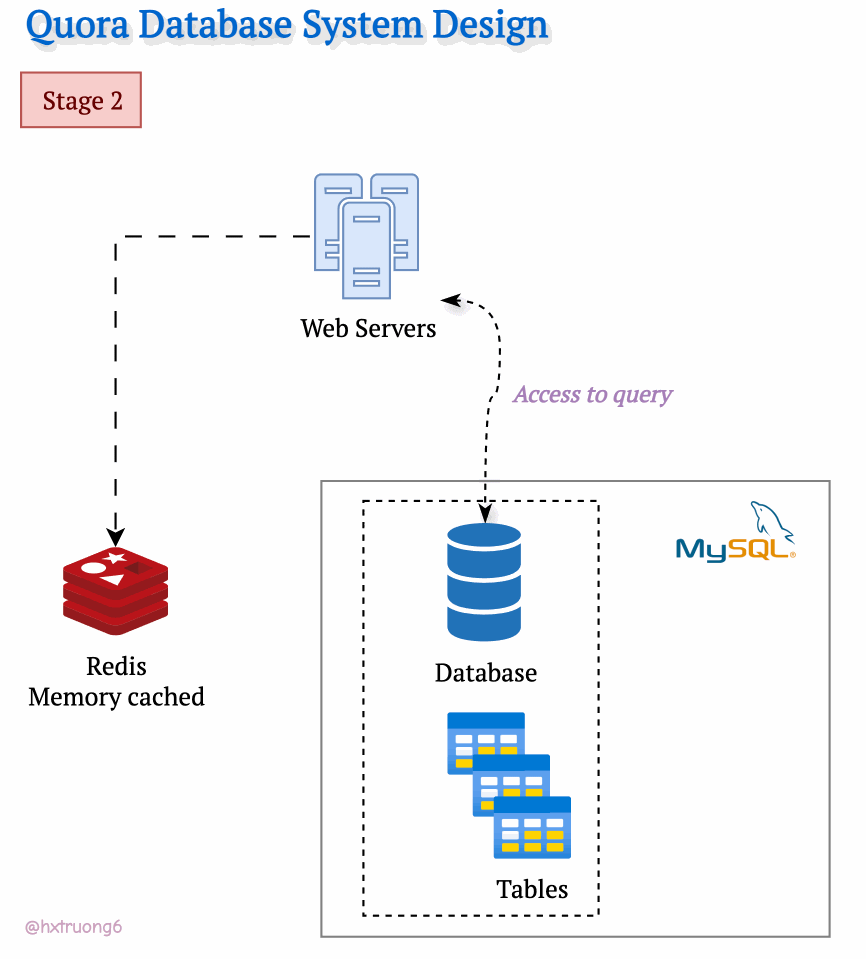
As Quora's popularity soared, more and more users flocked to the site. To keep up with the demand and ensure a smooth user experience, Quora's engineers likely turned to caching. They might have introduced a memory cache like Redis to quickly access frequently used data. Redis reduces the load on the MySQL database, especially as traffic increases.
Curious Section: What kind of data Quora could be cached?
Think about it: popular questions, trending topics, even user profiles could all be candidates for caching!
Data Growing Up
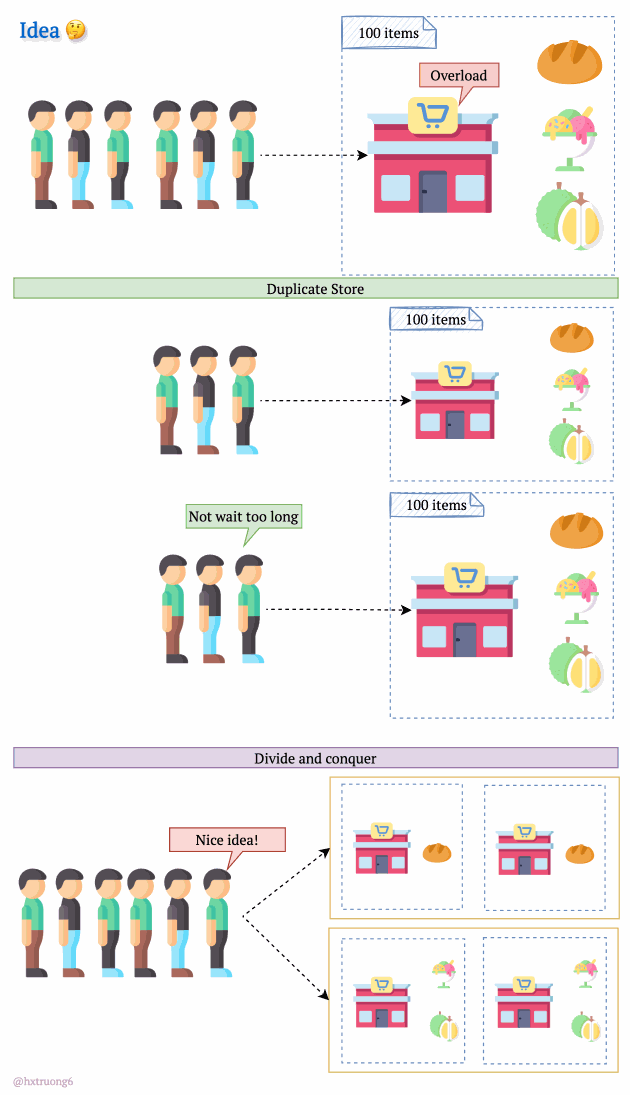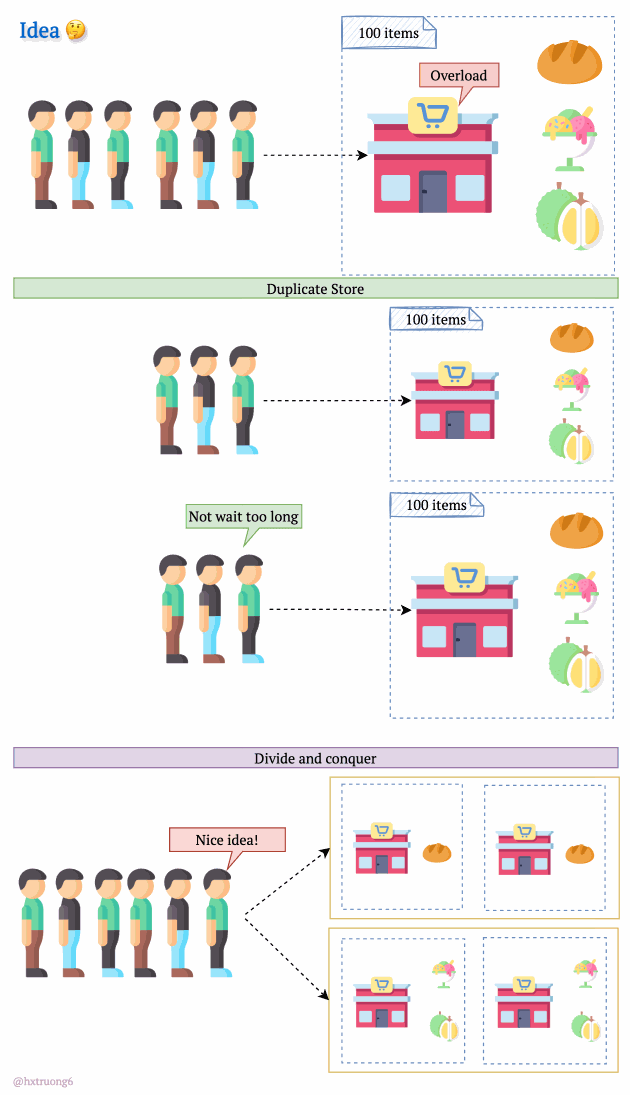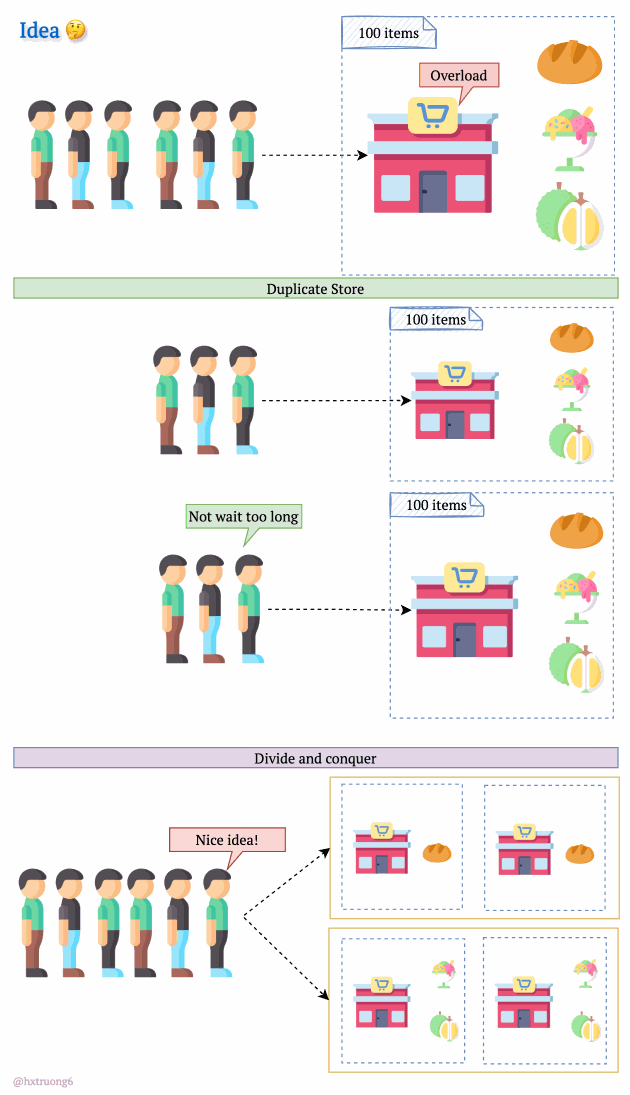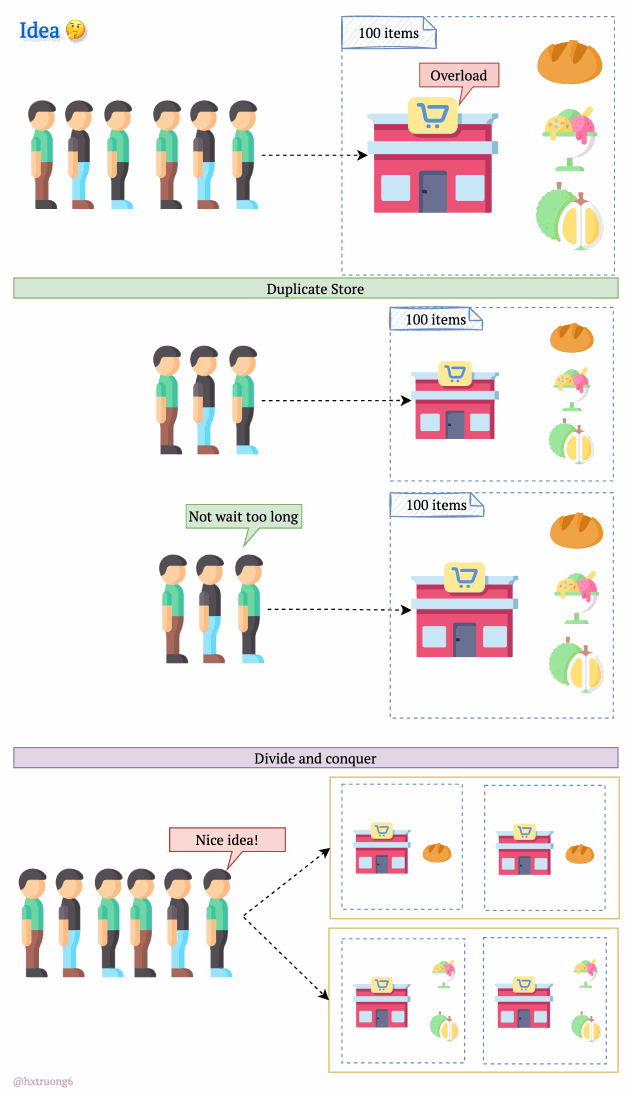
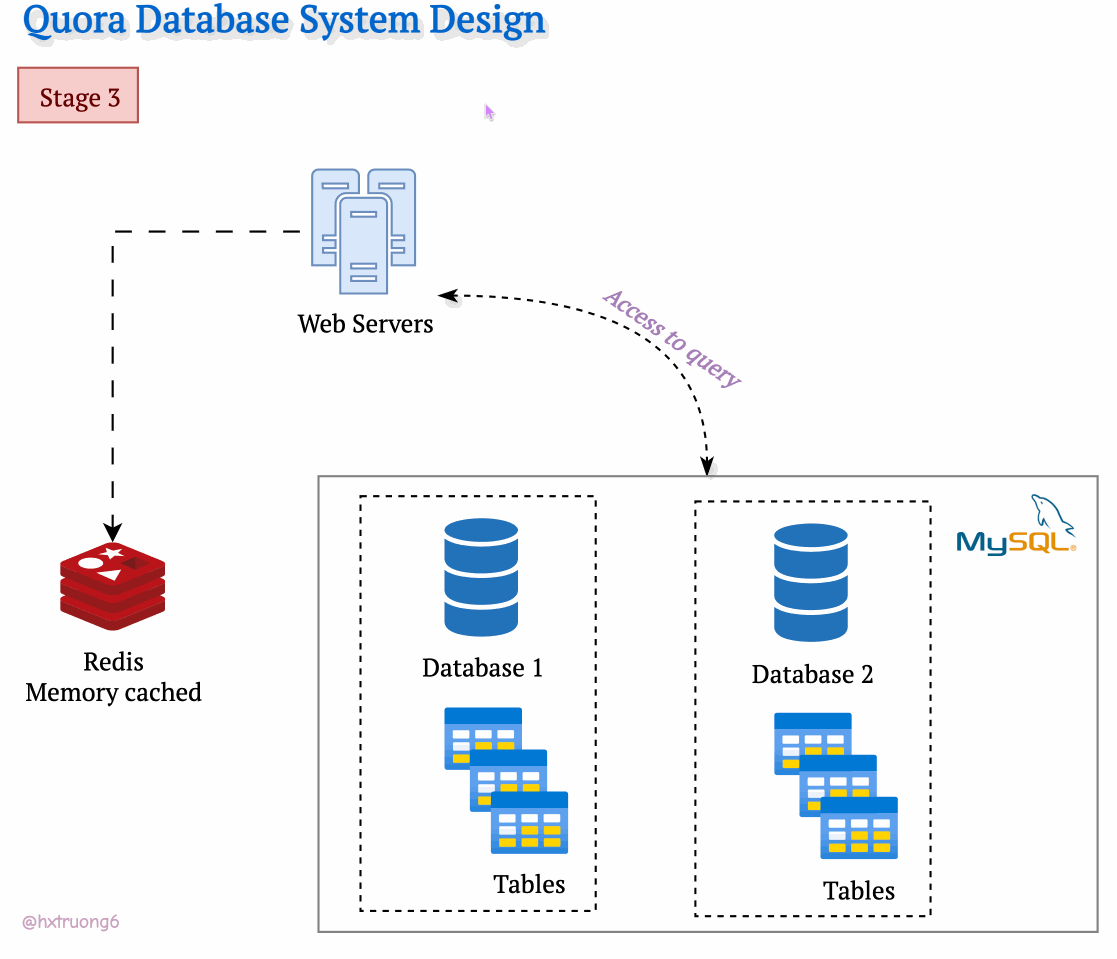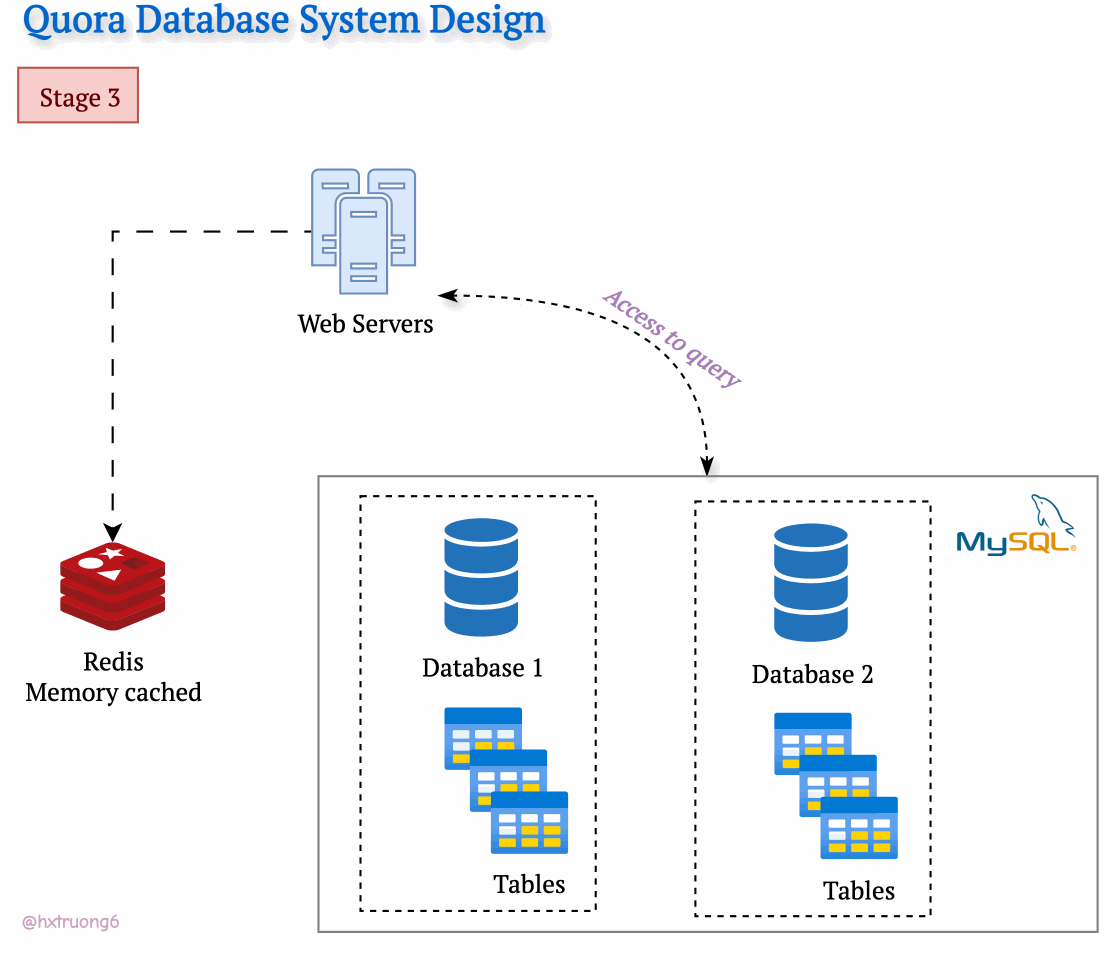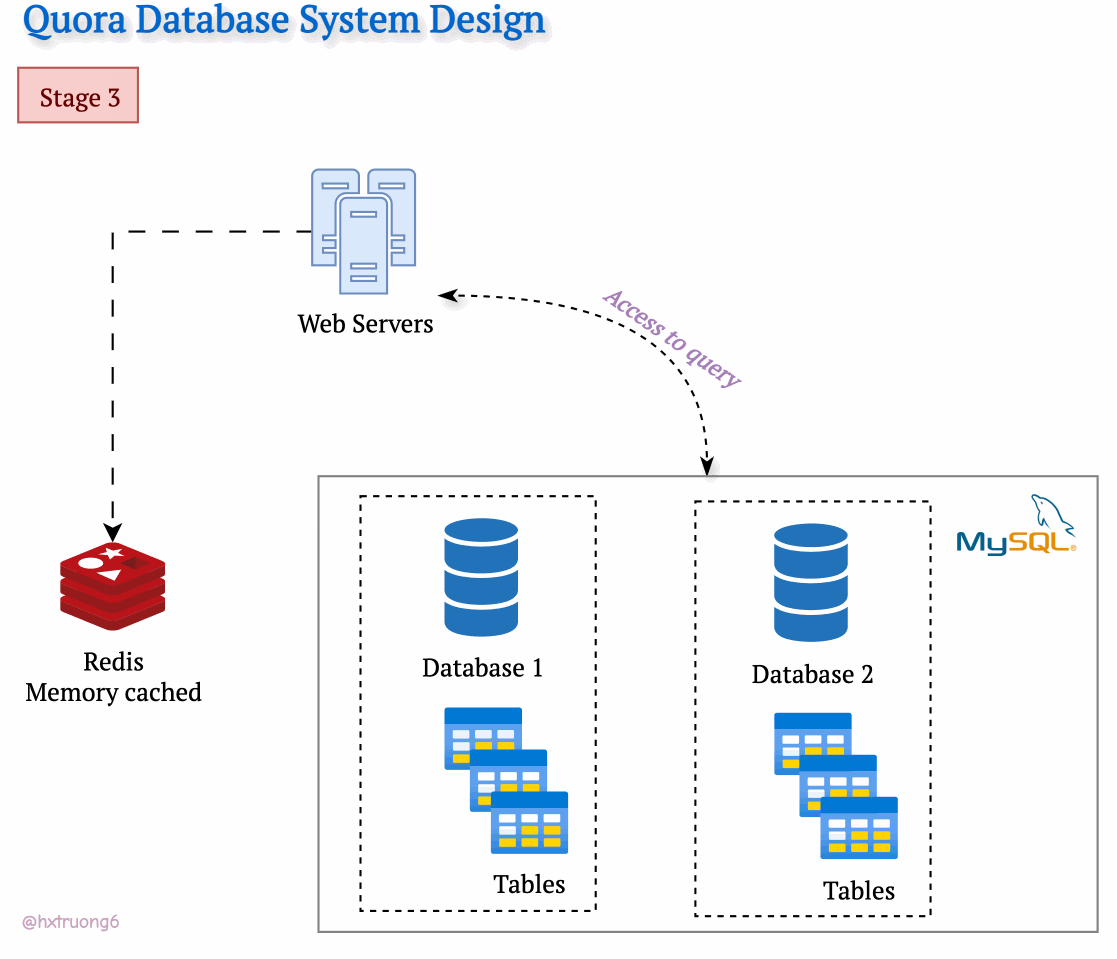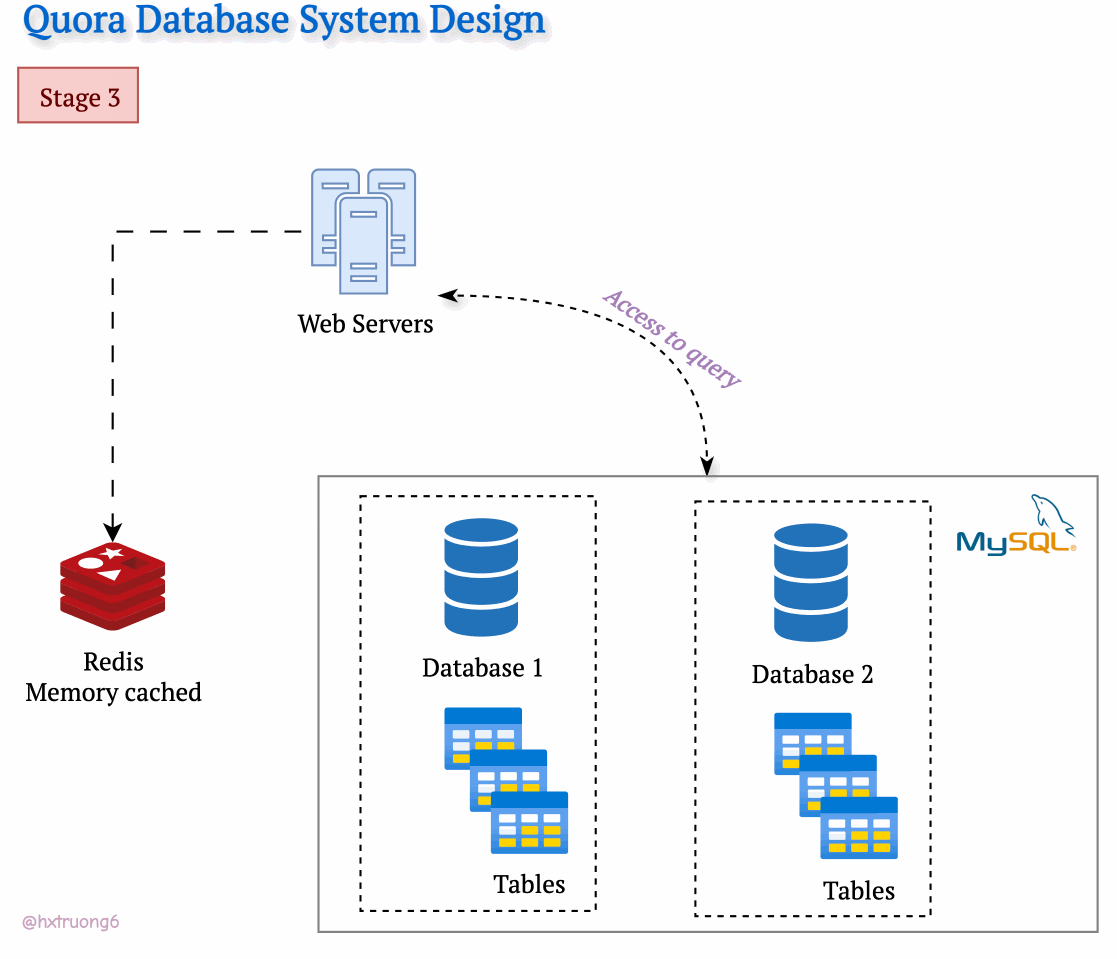
As expected, with a growing user base, Quora faced a surge in data that needed to be stored and queried. A single database, much like a single supermarket, would struggle during peak times, potentially leading to slowdowns or even downtime.
Similarly, adding more database servers could ease the load and handle more requests.
But wait! There's a crucial decision:
Option 1: Duplicate Everything? Replicate the full database schema (with all its tables) on each new server.
Option 2: Divide and Conquer? Split the data logically, so different databases are responsible for specific tables.
How do you think Quora might have approached this?
Data Explosion
At this stage, the data volume exploded, posing a challenge even with multiple databases in place. What's the next step?
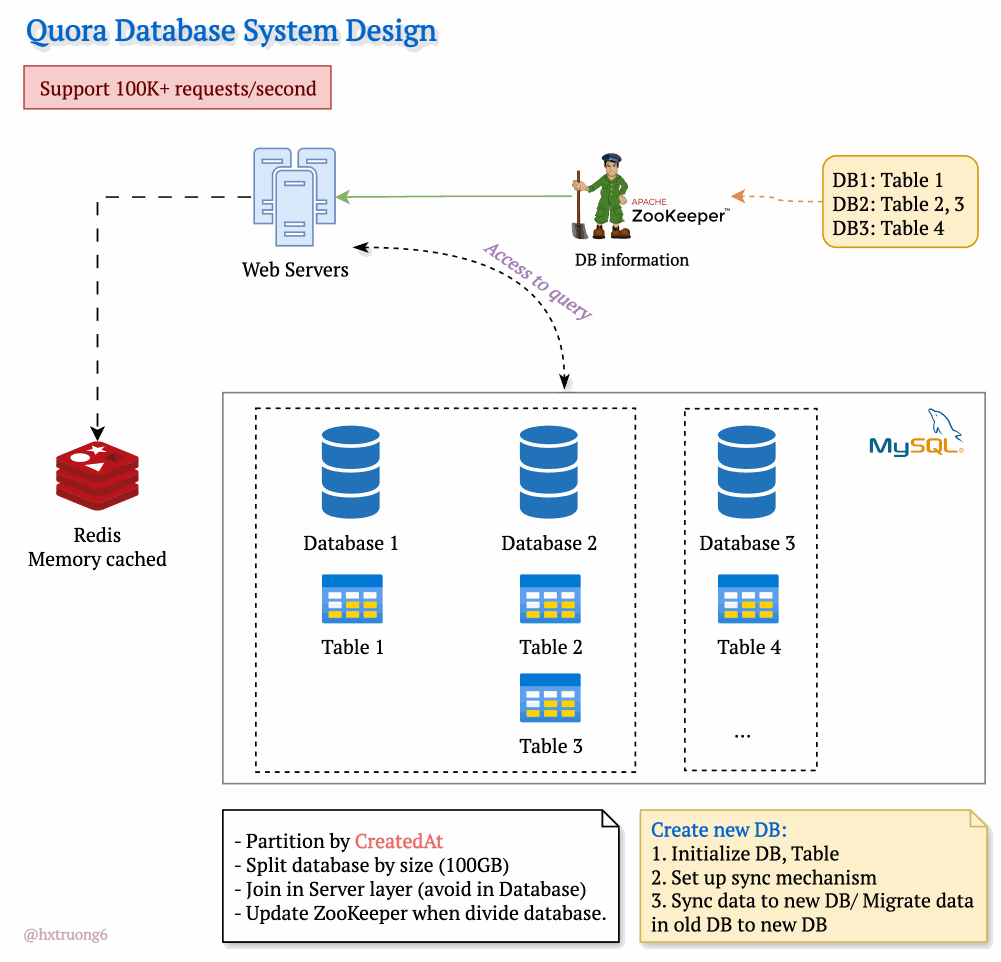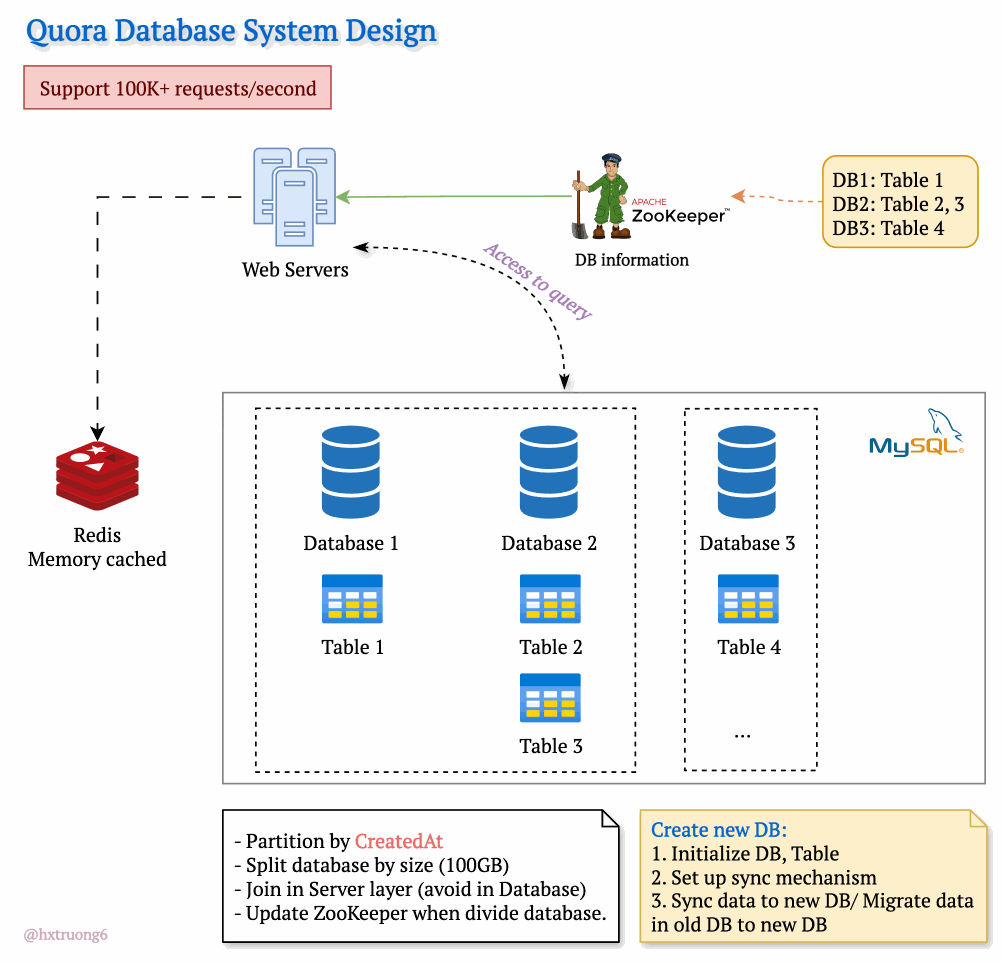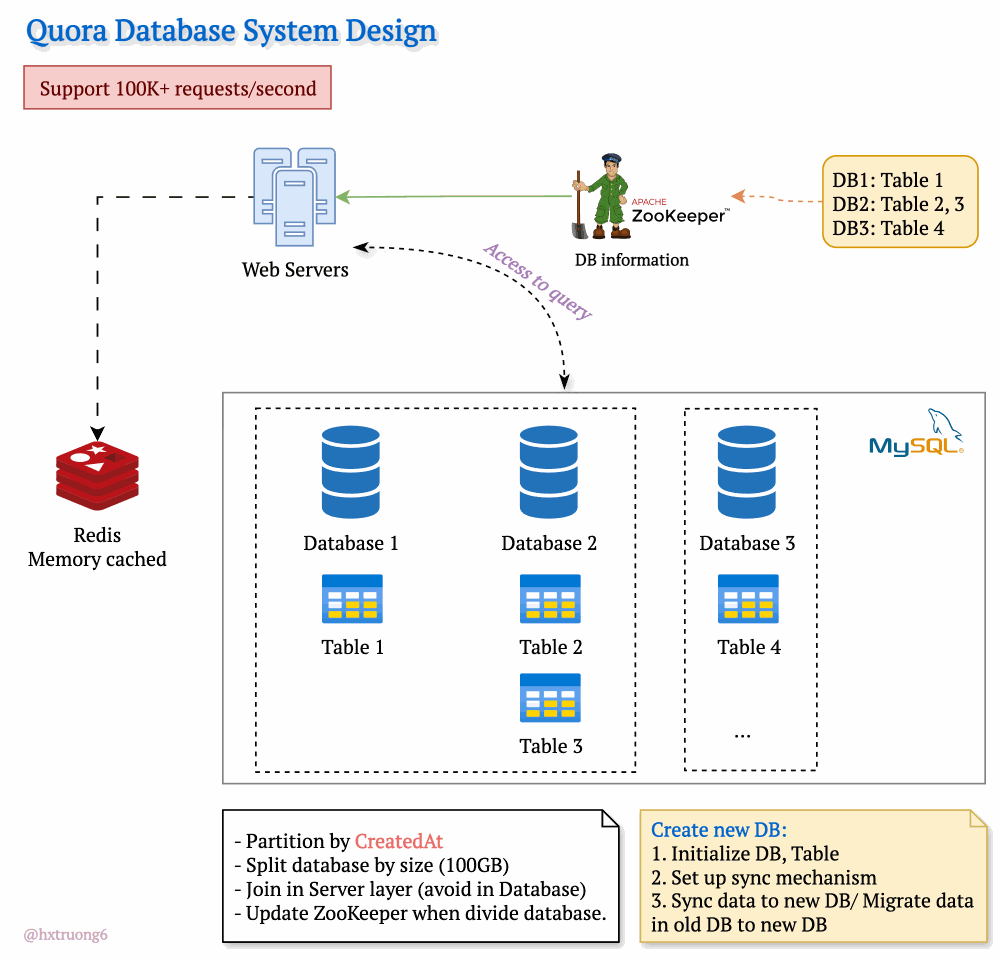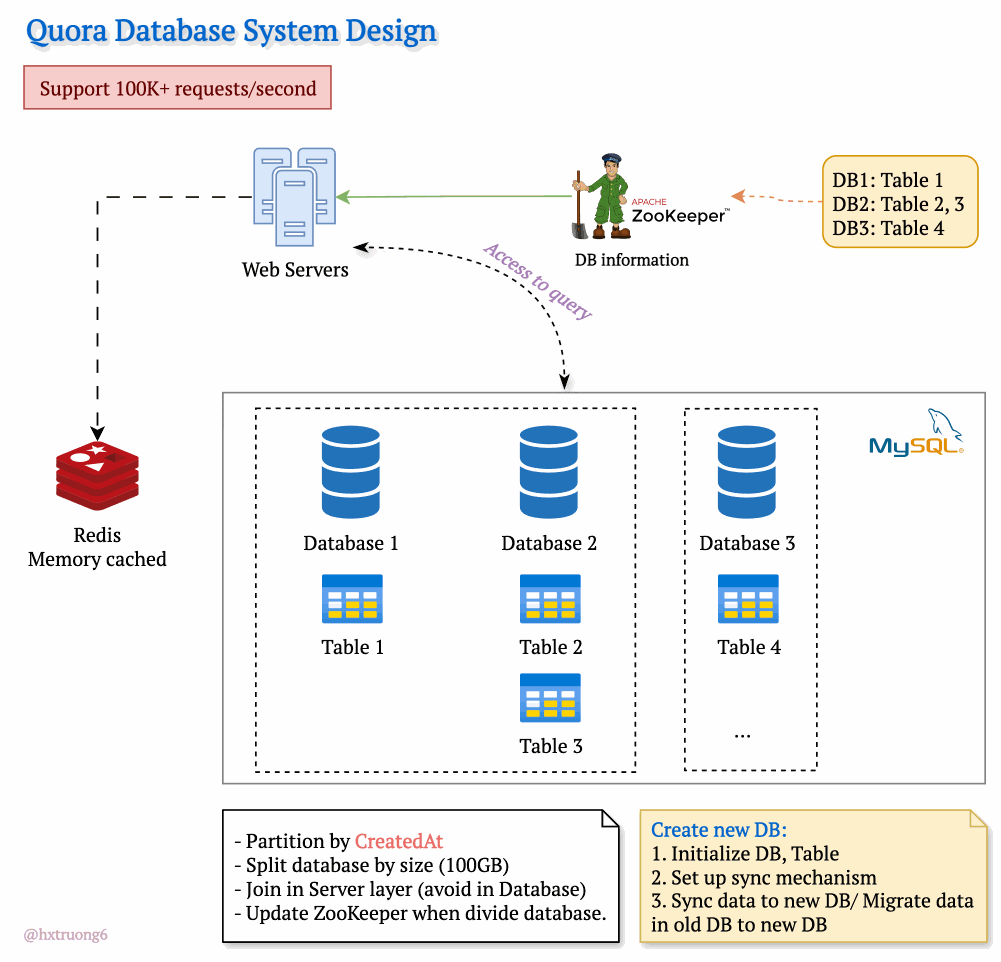
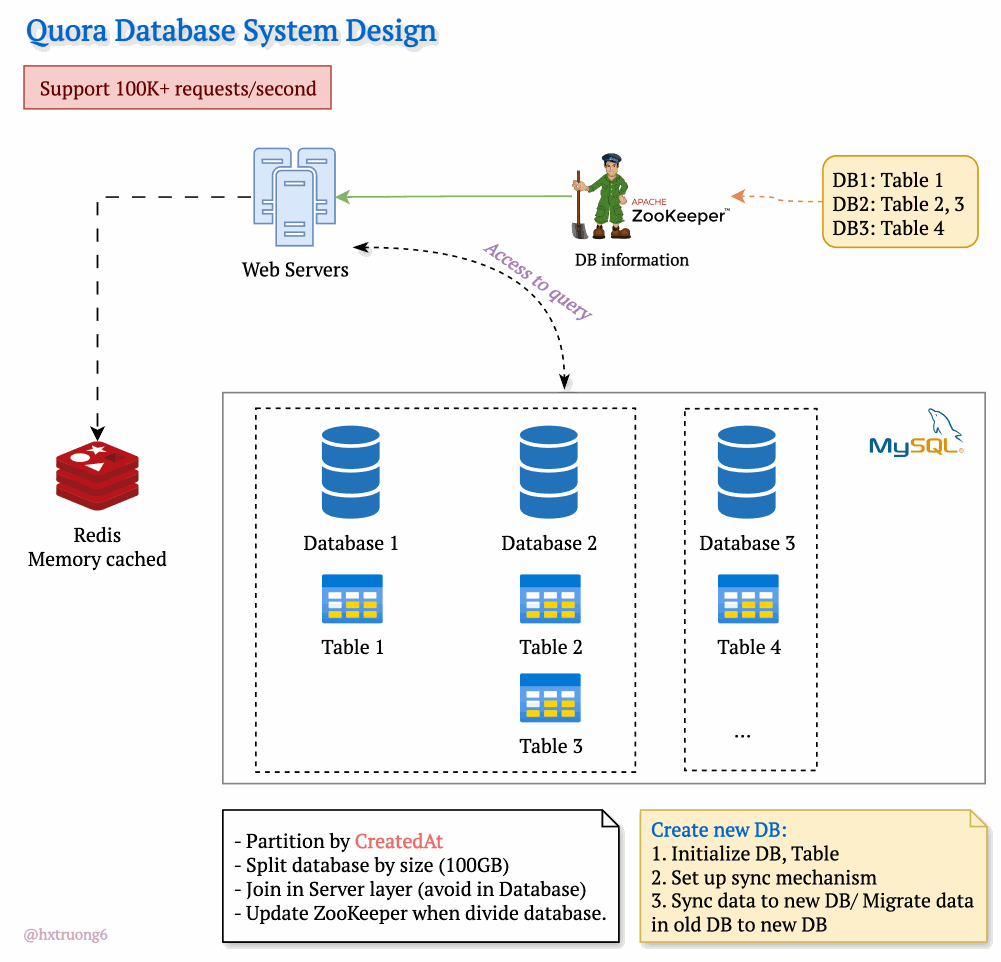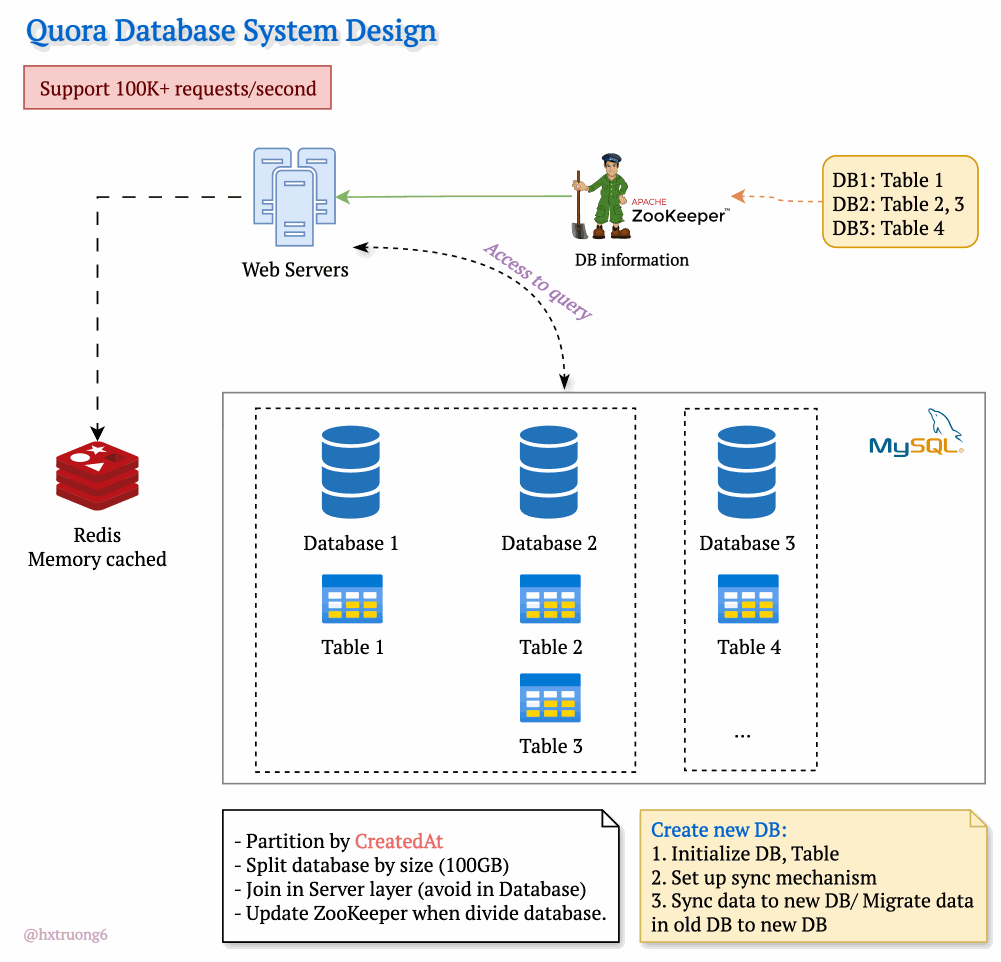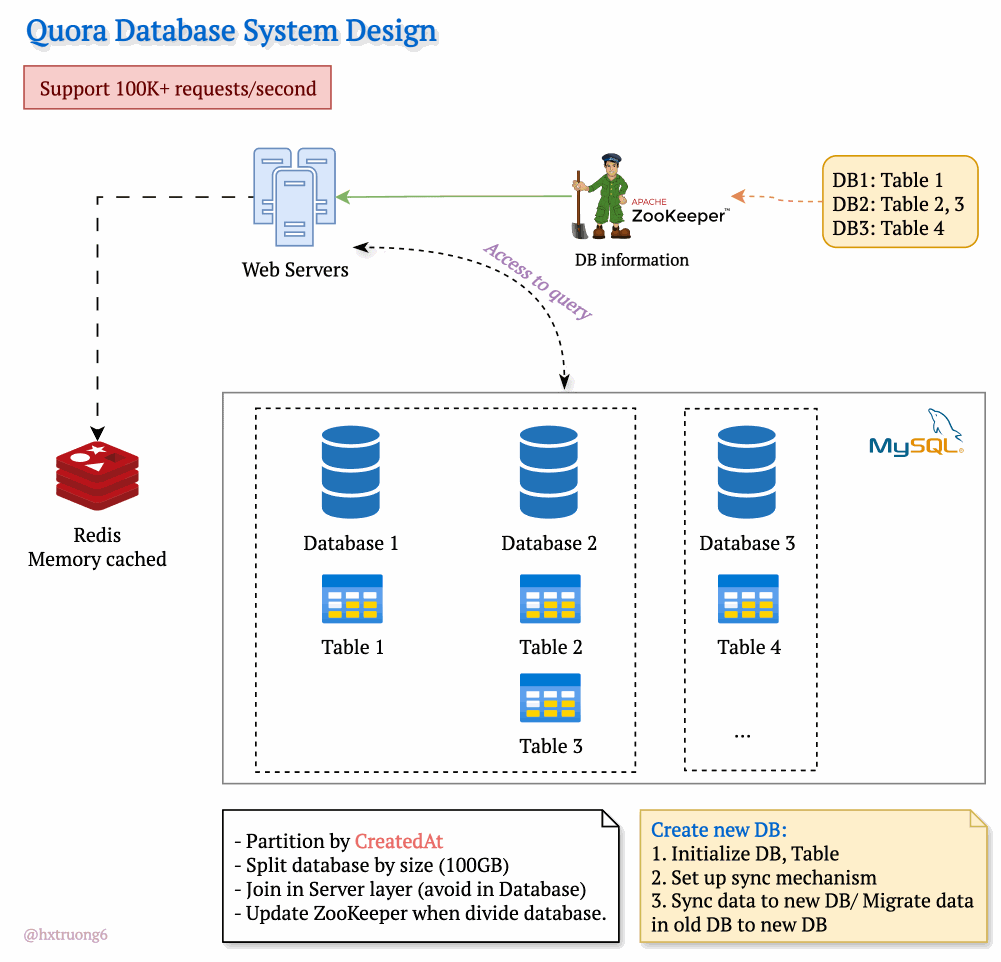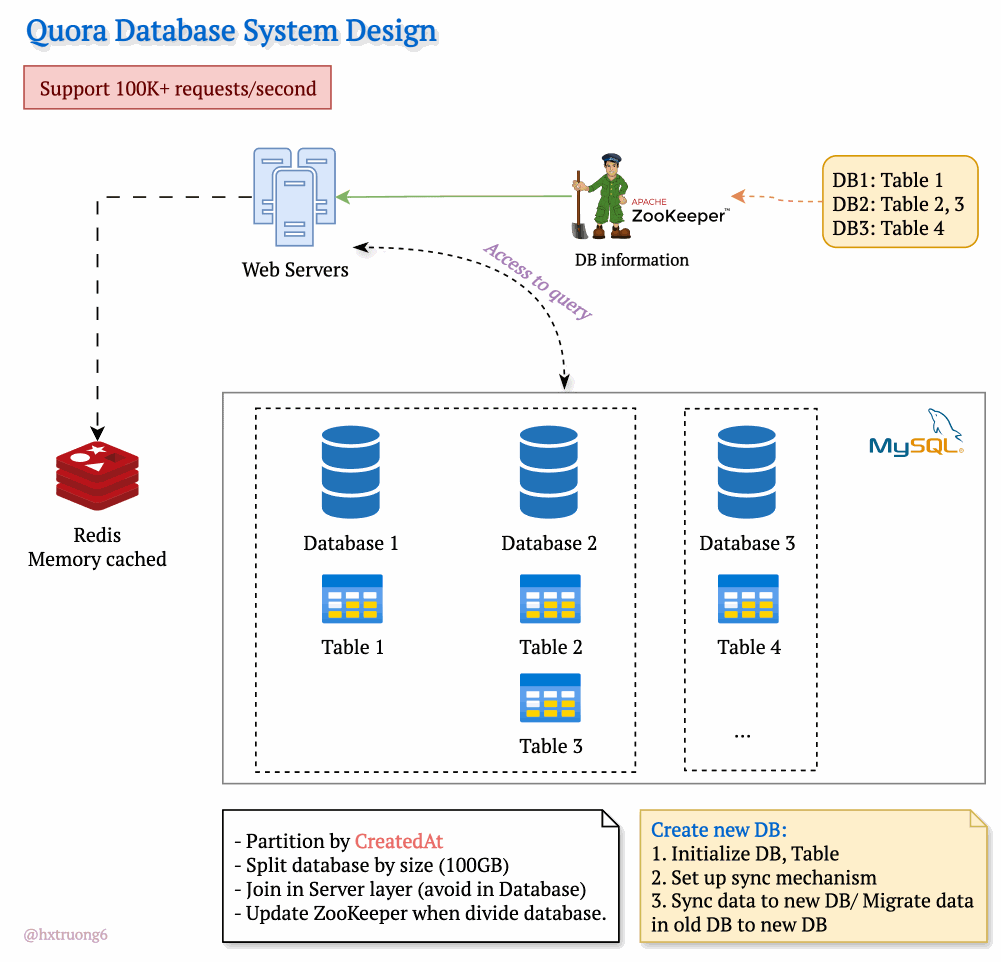
Drawing from our earlier discussion, Quora could combine database strategies for maximum benefit. This means using sharding - where some databases remain responsible for specific tables (like table 1), and those databases themselves could be replicated for redundancy.
With this architecture, if you need information from table 1, you query the designated table 1 databases. Need data from tables 2 and 3? Those queries go to their specific group of databases. This tackles overload by sharing resources and distributing queries across servers.
In summary:
Tables are divided across different databases, specializing their contents.
These databases reside on different servers for distributed power.
Curious Section: How do we query data from table 1 in database 1 and table 3 in database 2, when they reside on separate systems?
Database Configuration Information
How does the web server know where to find the right data within this network of databases? Enter ZooKeeper! This tool acts as a centralized coordinator, keeping tabs on database configurations. Whenever changes occur, ZooKeeper updates its records. It knows exactly where table 1 lives, where to find table 3, and so on.
Armed with this knowledge from ZooKeeper, the web server can intelligently collect data from different databases, assemble the necessary information, and respond to the user's request.
Note: ZooKeeper is a powerful tool in distributed systems, handling configuration, synchronization, and more!
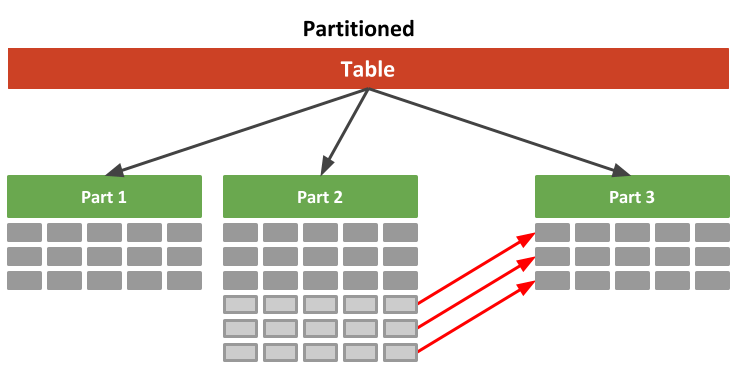
Optimization: Database Partitioning Strategies
To manage the massive data volume, Quora could partition databases in several ways:
createdAt (by year): Databases hold data for specific years (2021, 2022, etc.). This makes searches within a time frame more efficient.
Size-Based: If a database grows beyond a certain threshold (like 100GB), it's further divided to keep individual databases manageable.
ZooKeeper remains vital! It tracks these partitions, ensuring queries go to the right place.
The "Divide and Conquer" Mindset: Partitioning breaks down a massive database into more targeted units, boosting performance.
Trade-offs: Complex queries spanning multiple partitions often require more work at the web server layer, potentially avoiding database joins for speed.
Database Creation Process
When a new partition is needed:
Initialize DB, Table: Setting up the structure.
Set up sync mechanism: Ensuring new data flows into the new partition.
Sync data to new DB/ Migrate data in old DB to new DB: (Explain the difference briefly)
Curious Section: How could Quora optimize searching for questions?
Think about: ranking search, personalize, understand language,….
Conclusion
Throughout the article, we've seen how the principles of scalability, data integrity (through MySQL's transactions), and handling immense data volumes shape a system like Quora's. Their success demonstrates the power of "divide and conquer" strategies, along with careful consideration of the trade-offs inherent in distributed system design.
Remember, even if you're not building the next Quora, these concepts apply to countless projects. Whether it's a personal website or a complex application, understanding how to manage growing data sets is a crucial skill for any developer or tech enthusiast.
References
Thiết kế Database đáp ứng 400 triệu người tại Quora | System Design Wecommit